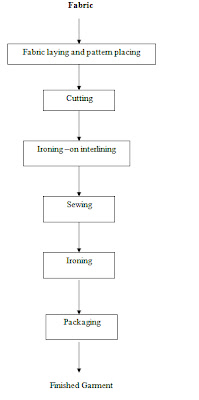
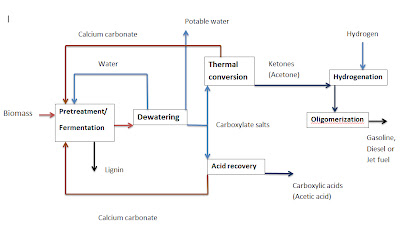
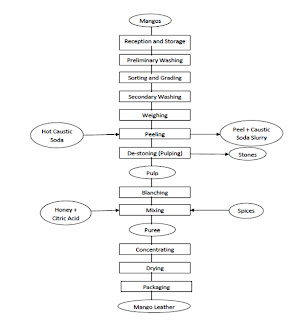
Production processes for manufacturing
polyester fibers and yarns, as explained in the following:
Production of ester building unit
In this process a chemical reaction is
carried out between monoethylene glycol and dimethyl terephthalate to produce
diglycol terephthalate.
Polymerization
In this process (for fiber
production) polymerization occurs to diglycol terephtalate to produce
polyester polymer.
Spinning
In this process, molten polyester
polymer is pumped to the spinnerettes and the filaments come out to meet a
stream of cold air and get solidified. The resulting filament tows collected